At present, most of the fastening connections used in vehicles are ordinary hexagon bolts, hexagon nuts, spring washers and other fasteners. In order to let you know more about the connection of bolts and nuts of automobile fasteners, we will share the information about the locking situation of bolts and nuts of ordinary fasteners, the failure analysis of bolts and nuts of ordinary fasteners, and the comparison of several kinds of locking nuts for vehicles.
1. Locking condition of bolts and nuts of ordinary fasteners
The main types of nut anti loosing structure are: hexagonal flange nut to increase the contact area; non-metallic insert hexagon locking nut and non-metal hexagon flange locking nut are prevented from loosing by inserting; all metal hexagon lock nut and all metal hexagon flange locking nut increase effective torque through head flange; hexagon slotted nut adopts split pin mechanical backstop.
Gasket anti loose structure is mainly: back-up and increase elasticity, spring washer, conical elastic washer, external serrated lock washer, etc. In the construction, thread gluing and mechanical locking are also commonly used, such as tightening bolts with holes with iron wire, locking plate locking and other anti loosening measures.
2. Failure analysis of bolt and nut of common fastener
The frame is the load-bearing body of various parts of the car, and each part is directly or indirectly fastened on the frame. As a sports equipment, the vehicle is affected by the load and road force, and the deformation of the frame and the loosening of the fasteners are natural.
The failure analysis of fastener connection is firstly analyzed from the working mechanism. During assembly, the tightening torque of wrench is converted into the pre tightening force of thread through friction force, and the field quality control only checks the tightening torque. From this process, it can be concluded that the factors affecting the failure of fasteners are tightening tools, tightening torque, thread structure, fastener quality, connected parts, external force, design, etc.
If the indicated value of the tool is inconsistent with the actual value, the tool shall be inspected regularly; if the compressed air pressure does not meet the requirements, it shall be inspected and rectified; the bolts and nuts without special requirements shall be tightened by pneumatic wrench, and the bolts and nuts with special requirements shall be tightened with pneumatic wrench first, and then fixed value wrench shall be used for tightening again. The failure reason is simple, that is, the torque does not meet the technical requirements; The results show that the pre tightening force is directly determined by the friction coefficient of thread itself, and the conversion of tightening torque into pre tightening force is also different under different pressure angles; the quality of fasteners, such as forging burst, dimension out of tolerance, friction coefficient deviation, etc.; the factors of connected parts include the quality of surface paint film, the thickness of paint film, the gap between the connected parts, and the elasticity of the connector; The main external force factors are vibration, impact, stress deformation, etc.; the design factors are improper selection of fasteners, too small or too large pre tightening force, shear force and tensile length deformation can not meet the actual needs.
According to the force analysis of the tightening process, the tightening torque needs to overcome the friction torque of the tightening end face, the friction torque of the thread pair and the elastic deformation torque of the connected parts, and the remaining part can be converted into clamping force. Therefore, under the same service conditions, the key factors determining the tightening force should be the structure and essential quality of the thread itself, such as structure, material, heat treatment, surface treatment, quality control, etc.
It can be seen that the failure of fasteners is mainly manifested in looseness, adhesion, deformation, wire shedding and fracture, resulting in loose fixation, disassembly and damage of the connected parts, and even causing traffic accidents, causing personal injury and property loss, such as the front part of the transmission shaft falling off, the front end landing on the ground to prop up the vehicle and causing rollover, and the steering spline shaft bolt falling off causing steering failure. Fastener seems to be a small part in the automobile structure, but fastener assembly is the main work of the whole vehicle assembly, and there are many varieties and large quantities, which are important factors affecting the whole vehicle assembly.
3. Comparison of several kinds of locking nuts for vehicles
3.1 ordinary hexagon nut
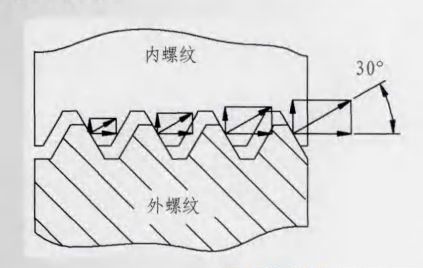
Ordinary hexagon head bolts and nuts will still be the mainstream of automotive fasteners due to their large batch production, mature technology and low cost. For many years, many fastener manufacturers have been committed to the research of thread looseness prevention, and have made special analysis on the loosening of ordinary hexagon bolts and nuts. The factors affecting the preload of ordinary hexagon nuts in the manufacturing process are mainly analyzed. The main factors affecting the pre tightening force are tooth shape, friction coefficient, etc, During thread engagement, most of the load is concentrated on the thread surface of the first and second teeth, which is unevenly distributed, and the dispersion of friction coefficient is large (see Fig. 1). Users often misunderstand that the greater the friction force, the better. In fact, the smaller the friction coefficient between the friction pairs and the greater the axial clamping force, the better the tightening performance. According to the theory that the influence of the change of friction coefficient on tightening efficiency and tightening degree presents the change trend of "shear difference", and through the test verification, the "median" friction coefficient is adopted, that is, the friction coefficient smaller than the current bolt and nut, we call it small friction coefficient. However, it is impossible to maintain a fixed value for all parts in mass production. Through the joint design of public relations with suppliers and process improvement, the friction coefficient can be kept within a reasonable range as far as possible.
3.2 never loosen the nut
The fasteners produced by many enterprises claim that they will never loosen, such as dtflock lock nut of the United States, hardlock lock lock nut of Japan, DISC-LOCK lock lock washer of the United States, nord-lock lock lock washer of Sweden, etc. Through the comparison, we choose to use the small friction coefficient nut for comparison, dtlock lock nut and hardlock lock lock nut from Japan.
1) Dtlock nut
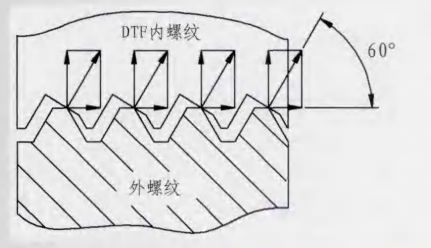
There is a 30 ° wedge-shaped inclined plane at the tooth bottom of the internal thread of dtlock nut. When the bolt and nut are tightened, the tooth tip of the bolt is tightly pressed against the wedge-shaped inclined plane of the nut, thus producing a great locking force. Due to the change of the angle of tooth shape, the normal force produced by the contact between the threads forms an angle of 60 ° with the bolt axis (see Fig. 2), instead of the 30 ° angle like that of the ordinary thread. The normal pressure of the dtflip thread is far greater than the fastening pressure, so the anti loosening friction force generated must be greatly increased.
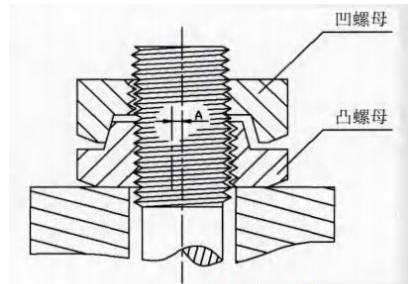
2) Hardlock nut
Hardlock is a double nut (see Fig. 3). The outer side of the inner nut is provided with an eccentric protrusion; the outer nut is a common nut structure with concentric grooves on its inner side; when the outer nut is tightened, the outer bulge of the inner nut is not concentric with the bolt, and the eccentric protrusion of the inner nut and the bolt are squeezed by the tightening of the outer nut to produce radial force, which is equivalent to adding a wedge in the thread gap and locking the thread in all directions.